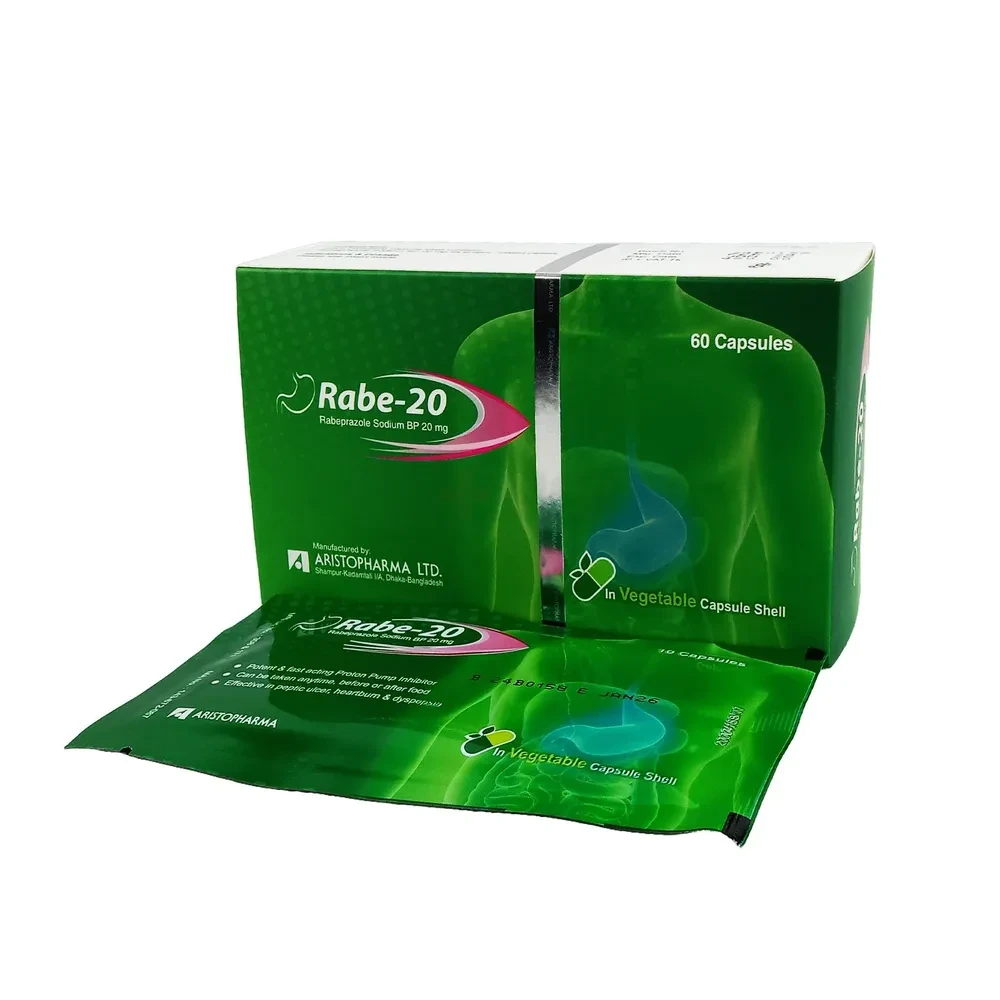
Description
• রেজিস্টার্ড চিকিৎসকের পরামর্শ মোতাবেক ঔষধ সেবন করুন
Indications:
-
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
-
Duodenal and gastric ulcers
-
Zollinger-Ellison syndrome
-
Erosive esophagitis
-
Maintenance therapy after healing of erosive esophagitis
-
Helicobacter pylori eradication (with antibiotics)
Pharmacology:
Rabeprazole inhibits the H+/K+ ATPase enzyme in gastric parietal cells, reducing acid secretion and promoting healing of acid-related mucosal damage.
Dosage & Administration:
-
Typical dose: 20 mg once daily before meals, usually in the morning
-
Duration varies with condition: 4–8 weeks for GERD; 4–6 weeks for ulcers
-
For H. pylori eradication: 20 mg twice daily with antibiotics for 7–10 days
-
Swallow whole; do not crush or chew
Interaction:
-
May affect absorption of drugs requiring acidic environment (ketoconazole, atazanavir)
-
Can increase blood levels of digoxin, warfarin, cyclosporine
-
Caution with methotrexate due to delayed clearance
-
Antacids do not affect Rabeprazole efficacy
Contraindications:
-
Known hypersensitivity to Rabeprazole or related compounds
-
Severe hepatic impairment without medical supervision
-
Use with rilpivirine-containing drugs
Side Effects:
-
Headache, diarrhea, nausea, abdominal pain
-
Constipation, flatulence
-
Rare: Vitamin B12 deficiency, hypomagnesemia, fractures with long-term use
-
Skin rash, liver enzyme elevation (rare)
Pregnancy & Lactation:
-
Use only if clearly needed during pregnancy
-
Excreted in breast milk; use caution when breastfeeding
Precautions & Warnings:
-
Long-term use may increase gastric cancer risk
-
Monitor magnesium levels during prolonged therapy
-
Evaluate for H. pylori infection in recurrent ulcers
-
Adjust dose in hepatic impairment
Therapeutic Class:
Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs)
Storage Conditions:
Store below 30°C in a dry place, away from light and moisture. Keep out of reach of children.




.webp)



































.webp)









 1000 MG.jpg)




























.webp)
 4ML.jpg)

.jpeg)





.jpeg)