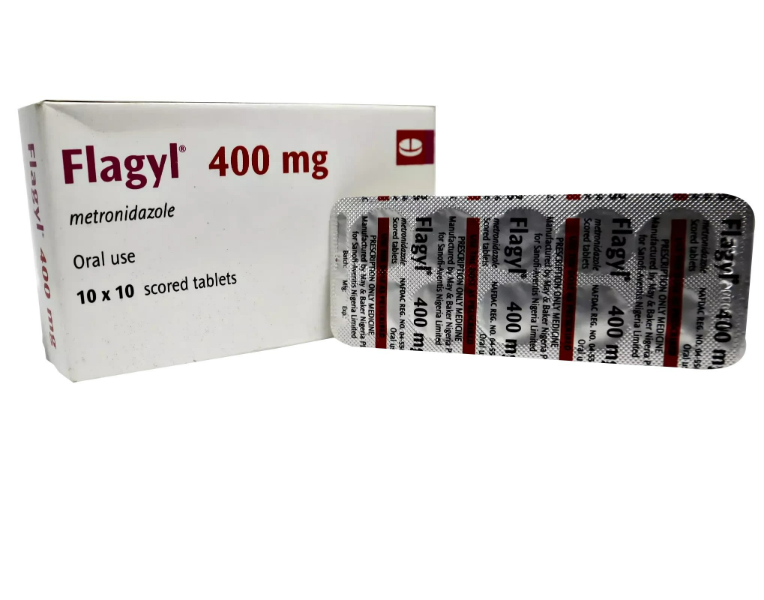
Description
• রেজিস্টার্ড চিকিৎসকের পরামর্শ মোতাবেক ঔষধ সেবন করুন
Pharmacology:
-
Metronidazole is a nitroimidazole antimicrobial agent that is selectively toxic to anaerobic organisms and protozoa.
-
Once inside anaerobic cells, it is reduced to active metabolites that bind DNA and inhibit nucleic acid synthesis, leading to microbial cell death.
Dosage:
-
Adult dosage: 850 mg 2-3 times daily, depending on infection severity and type.
-
Dosage and duration should be guided strictly by physician recommendation.
-
Renal and hepatic impairment may require dose adjustment.
Administration:
-
Take orally with a full glass of water.
-
Can be taken with or after meals to reduce gastrointestinal discomfort.
-
Complete the full course even if symptoms improve early.
Interaction:
-
Do not consume alcohol during and for 48 hours after treatment – risk of disulfiram-like reaction (nausea, vomiting, cramps).
-
Can interact with:
-
Warfarin – increased bleeding risk
-
Lithium – risk of toxicity
-
Enzyme inducers like phenytoin, phenobarbital – reduced efficacy
-
Cimetidine – may increase plasma metronidazole levels
-
Contraindications:
-
Hypersensitivity to Metronidazole or other nitroimidazoles
-
History of blood dyscrasias or central nervous system disorders
-
Use with caution in patients with hepatic encephalopathy or epilepsy
Side Effects:
-
Common: Nausea, metallic taste, dry mouth, dizziness, headache
-
Less common: Diarrhea, loss of appetite, dark urine
-
Serious (rare): Neuropathy, seizures, allergic reactions, pancreatitis
Pregnancy & Lactation:
-
Pregnancy: Category B – use only if clearly needed, especially avoiding first trimester for trichomoniasis treatment
-
Lactation: Metronidazole is excreted in breast milk. Consider pausing breastfeeding or consulting a physician for risk assessment



.jpg)